As is known to all, 7.0 mmol/L is the red line of fasting blood glucose (FBG). When FBG is above the red line, an examination will be recommended even if there are no symptoms of "three more and one less" (drink more, eat more, urinate more, but lose weight). If FBG is still above the red line after examination, such people may be diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (DM).
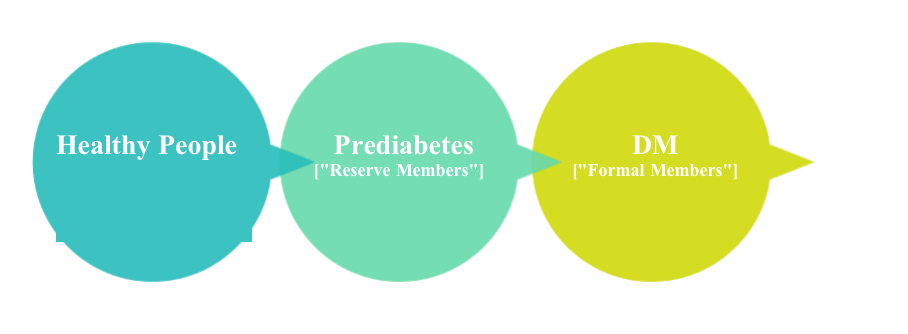
However, there is still a "grey zone" in the transition from healthy people to DM patients (FBG > 6.1 mmol/L), which refers to prediabetes. Those who develop prediabetes from healthy people are called "reserve members" of DM.
The symptoms of prediabetes include impaired fasting glucose (IFG) (FBG: 6.1 to 7.0 mmol/L) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) [2-hour postprandial blood glucose (2hPG): 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L].
Prediabetes is a dynamic clinical process from euglycemia to DM, which is a necessary phase for healthy people to develop into patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). As there is generally no symptom, prediabetes is not easy to be identified. However, it is an early warning signal of DM.
Studies have shown that the risk for prediabetes patients to develop DM is more than 8 times that of those with euglycemia after a 6.5-year follow-up. Therefore, such people can be described as "reserve members" of DM, who must not treat prediabetes lightly.
1. How to diagnose prediabetes?
Prediabetes will be diagnosed when any of the following three is met:
- FBG: 6.1 to 7.0 mmol/L.
- 2hPG after a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L.
People should eat normally 3 days before the OGTT and neither engage in strenuous activities nor smoke during blood examination.
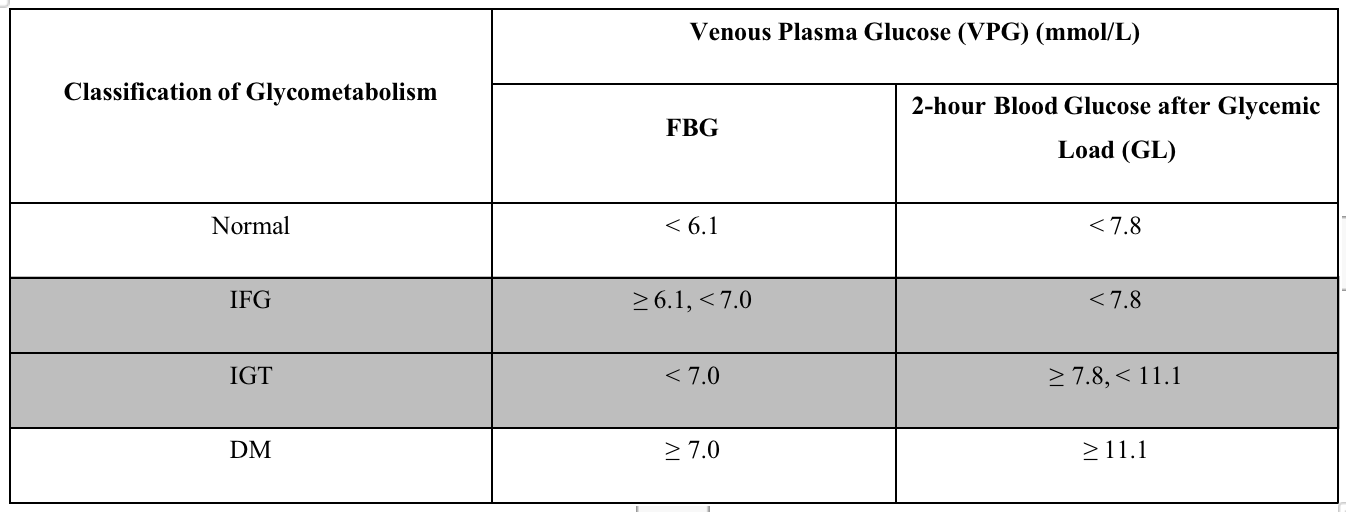
- Glycosylated hemoglobin: ≥ 5.7%.
Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) can reflect the level of blood glucose control in the recent 2 to 3 months, which is an important and stable indicator to weigh blood glucose level.
2. How to delay the progression of prediabetes?
A large number of studies have shown that some prediabetes patients can stay in this phase or even reverse it by changing their lifestyle (such as adjusting their diet and strengthening exercise) or taking other intervening measures to reduce the onset of T2DM.
To delay or terminate the progression of prediabetes, we should do the following:
1. Keep a healthy weight
We should lose excess weight by balancing our physical activities with appropriate nutrition. If not managed in time, obesity may induce T2DM.
2. Keep a good mood
Emotional stress may directly lead to islet β cell dysfunction, which will eventually fix the tendency of insufficient insulin secretion, thus inducing DM. Therefore, we should learn to get rid of stress and unsatisfactory things, trying to keep a stable mood and a pleasant state of mind.
3. Ensure adequate sleep
A study has shown that those who sleep for 7 to 8 hours every night are the healthiest. The risk for those who sleep for less than 6 hours every night to develop DM will increase by 2 times or so, while the risk for those who sleep for more than 8 hours to develop DM will increase by more than 3 times. Therefore, keeping regular work and rest is crucial to preventing DM.
4. Stick to a healthy diet and exercise
We should not eat high-fat and high-calorie foods but eat more fruits, vegetables, and coarse grains to ensure the fiber content in foods.
At the same time, we should exercise five days a week and such physical activities should not be too strenuous. A simple exercise for 30 minutes at a time is beneficial for health, such as walking. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) points out that the risk of T2DM can be reduced by 58% through moderate exercise for only 150 minutes a week.
5. Monitor blood glucose daily
This is a very important point that is often neglected.
No matter for those who have a family history of DM and prediabetes, or those who have developed into "formal members" of DM, the more they know about their blood glucose, the faster they can grasp the law of influence of daily diet, exercise, and drugs on their blood glucose. This also means that they can better regulate their blood glucose through daily behaviors, thus delaying or even terminating the progression of the disease.
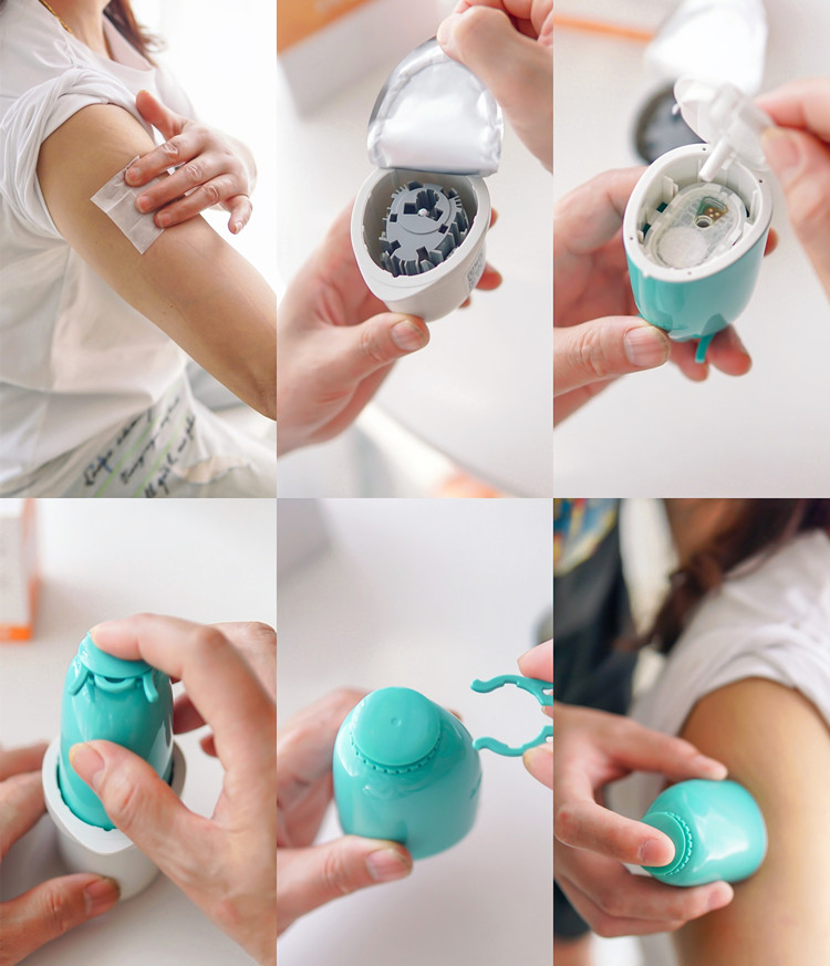
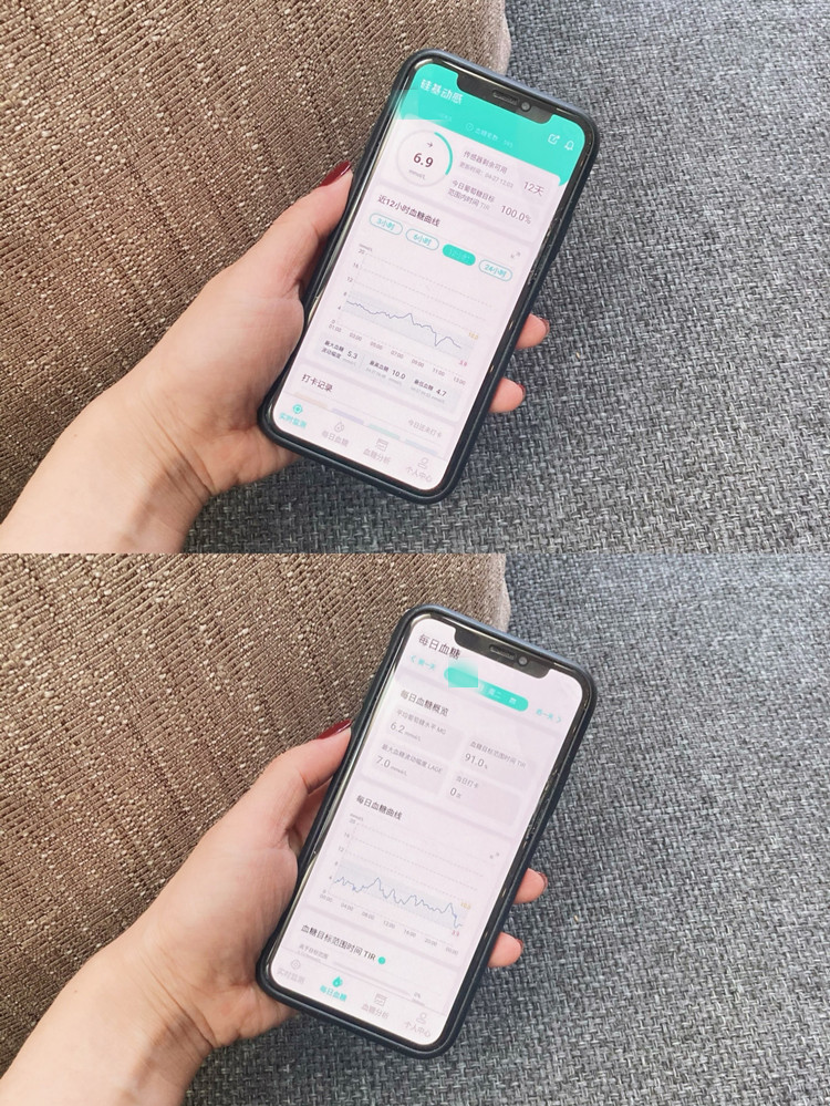
△ SIBIONICS CGM System has maximum IP level and no impact on daily life
The method commonly used to monitor blood glucose is to prick a finger to measure it, which can only reflect the blood glucose change at a certain time point.
However, human blood glucose is in a continuously changing process, which requires the combination of time points with time periods. Only by obtaining a continuous monitoring curve can the blood glucose change be truly and comprehensively reflected.
△ SIBIONICS CGM System divides blood glucose data into TIR value and estimated HbA1c
To sum up, those who have a family history of DM, suffer from prediabetes or DM, or have the demand for blood glucose monitoring are all recommended to monitor their blood glucose with SIBIONICS CGM System.
SIBIONICS GS1 CGM-Sistem de monitorizare continuă a glucozei

679.00 dh
Monitorizare continuă a glicemiei pe 14 zile Citiri foarte precise ale senzorului Rapoarte AGP exportabile Date de glucoză care pot fi partajate în timp real Alarma de glucoza personalizabila Aplicație ușor de utilizat Calibrare gratuită Fără scanare IP28 Impermeabil … read more